 Electrical safety is of paramount importance in the workplace, and it is crucial for electrical maintenance personnel to have a clear understanding of the hazards they may encounter. One of the most significant hazards that electrical maintenance workers may face is an arc flash. This blog will discuss what arc flash is, how it occurs, why electrical safety is so important, why compliance with NFPA 70E and OSHA is critical, and some best practices to prevent arc flash.
Electrical safety is of paramount importance in the workplace, and it is crucial for electrical maintenance personnel to have a clear understanding of the hazards they may encounter. One of the most significant hazards that electrical maintenance workers may face is an arc flash. This blog will discuss what arc flash is, how it occurs, why electrical safety is so important, why compliance with NFPA 70E and OSHA is critical, and some best practices to prevent arc flash.
What is Arc Flash in the Workplace?
Arc flash is a dangerous electrical phenomenon that occurs when an electric current jumps between two conductive objects. This phenomenon results in a release of energy in the form of light and heat, which can cause severe injury, burns, or even death. Arc flash can occur in any industry with electrical equipment, including manufacturing, construction, and maintenance.
How does Arc Flash Occur?
Arc flash occurs when there is a breakdown in the insulation between two conductive objects. This breakdown can be caused by a number of factors, including human error, equipment failure, or environmental factors such as moisture or dust. Once the insulation is breached, an electrical current can jump between the two conductive objects, resulting in an arc flash. When it comes to preventing arc flash, electrical safety is essential in the workplace because electrical hazards can result in severe injury or death. Electrical hazards can also cause significant property damage and result in costly downtime.
Why is it Important to Comply with NFPA 70E and OSHA?
Compliance with NFPA 70E and OSHA is critical for ensuring the safety of electrical maintenance personnel. NFPA 70E provides guidelines for electrical safety in the workplace, including requirements for training, personal protective equipment (PPE), and hazard assessments. OSHA provides a framework for developing and implementing safety procedures to protect workers from electrical hazards.
Some Best Practices to Prevent Arc Flash
Implementing best practices to prevent arc flash can help to reduce the risk of electrical hazards in the workplace. Here are some examples:
- Conduct a Hazard Assessment: Conducting a hazard assessment can help identify potential electrical hazards in the workplace and determine the appropriate PPE for electrical maintenance personnel.
- Use Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Lockout/tagout procedures can prevent accidental energization of electrical equipment during maintenance or repair.
- Provide Appropriate PPE: Providing appropriate PPE such as arc-rated clothing, gloves, and face shields can help protect electrical maintenance personnel from arc flash.
- Use Warning Labels: Warning labels can alert personnel to potential electrical hazards and provide information on proper PPE and safety procedures.
- Use Permanent Electrical Safety Devices (PESDs): PESDs are permanently installed voltage indicator and test point devices that improve safety and productivity when performing electrical maintenance procedures such as LOTO.
Arc Flash and Lockout/Tagout Compliance Statistics
According to the BLS, in 2019, there were 160 fatalities due to exposure to electricity, and 2,530 non-fatal injuries involving days away from work. Failure to follow LOTO procedures was one of the top 10 most frequently cited OSHA violations in 2022, with 1,977 violations.
Arc flash is a significant hazard that electrical maintenance personnel may encounter in the workplace. It is essential to comply with NFPA 70E 120.5 Process for Establishing an Electrically Safe Working Condition and implement best practices to prevent arc flash. By doing so, we can help to reduce the risk of electrical hazards and ensure the safety of all workers.
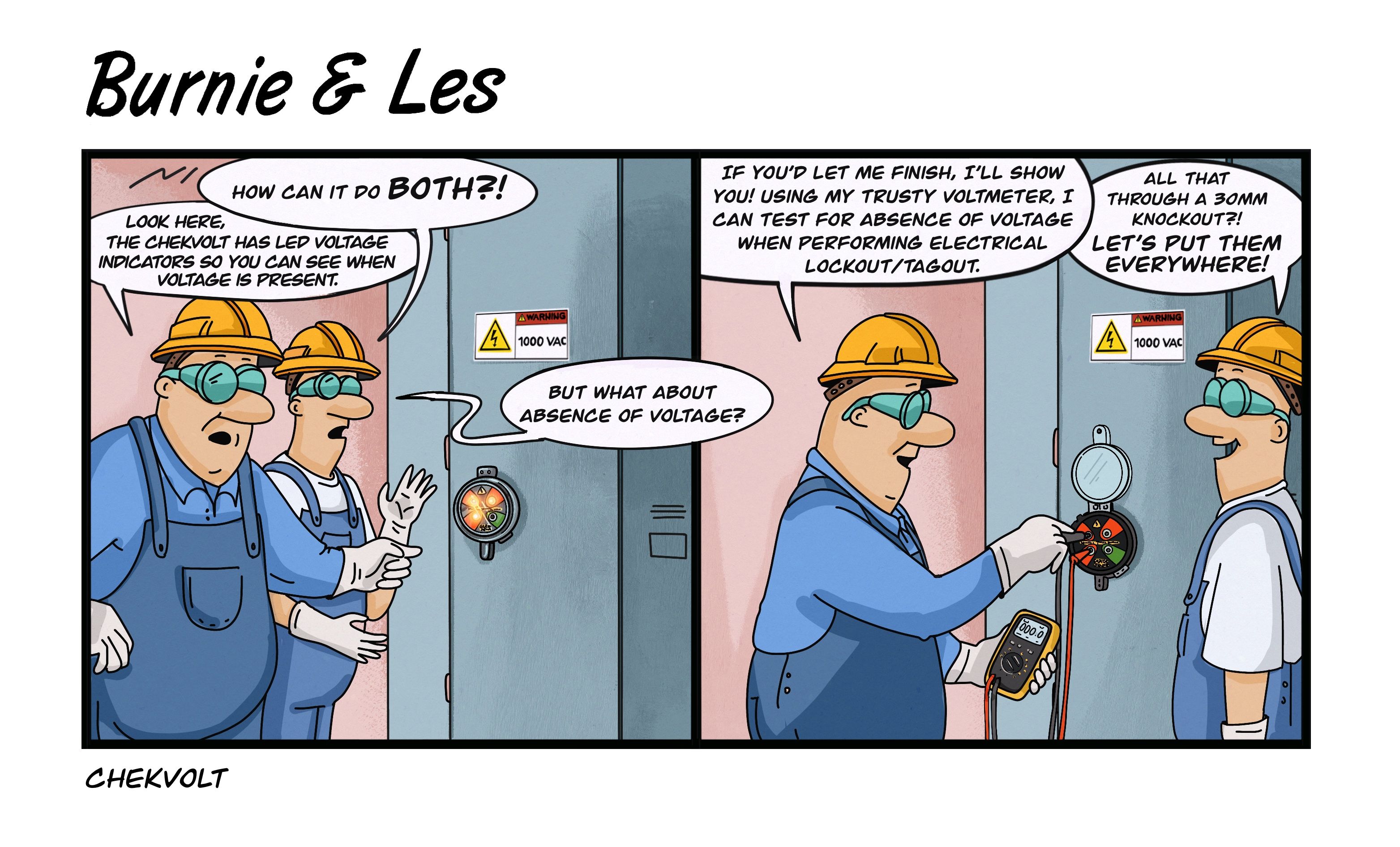
How the ChekVolt PESD Makes LOTO Safer, Smarter, and More Productive
Performing LOTO safely requires the answer to one question; is there voltage? NFPA 70E/CSAZ462 requires an absence of voltage test to verify an electrically safe work condition. The traditional process poses arc flash and shock hazards to comply with NFPA 70E Article 120.5: Process for Establishing
and Verifying an Electrically Safe Work Condition.
The ChekVolt allows you to test absence of voltage and provides voltage presence indication; all without opening the enclosure door. PESD users report LOTO procedure time reductions of 35-40 minutes. ChekVolt pays for itself after 6-8 LOTO procedures from time savings alone.
This touch-safe, compact PESD features voltmeter-compatible test points and redundant LED voltage presence indication rated up to 1000 VAC/VDC. The ChekVolt® is quickly installed through a single 30mm knockout and includes four lead wires potted in the construction–making LOTO in even the harshest environments safer, smarter, and more productive.


